Unveiling the Mysteries of NGC 2264
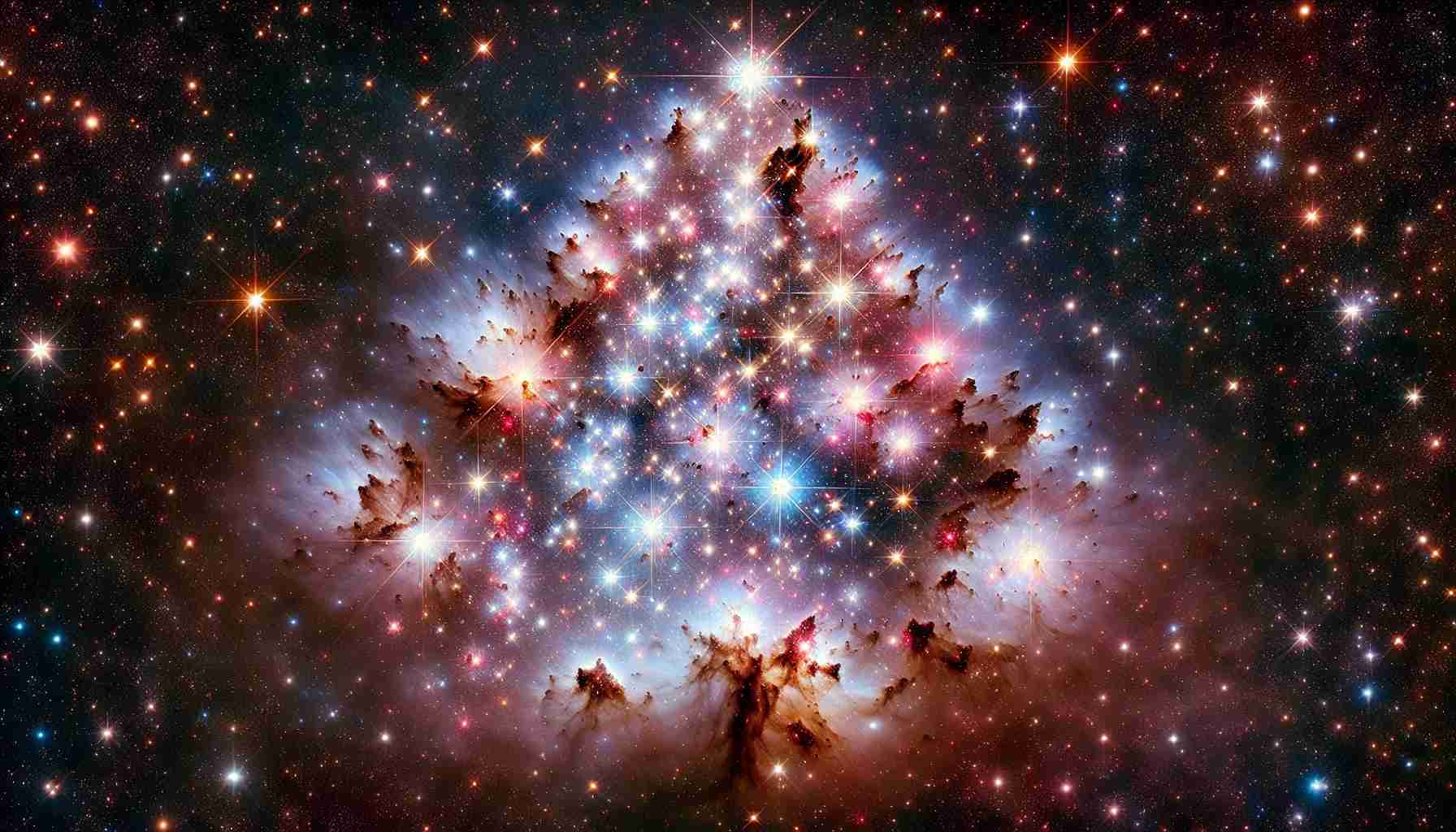
Recent findings reveal a stunning new perspective of the “Christmas tree cluster,” also known as NGC 2264. This celestial marvel, approximately 2,500 light-years away from Earth, showcases young stars that are between one and five million years old. The striking image, made available on December 17, 2024, combines advanced X-ray data from NASA’s Chandra X-ray Observatory with spectacular optical insights captured by astrophotographer Michael Clow from his telescope in Arizona.
In this enhanced visualization, the intricate details of the cluster come to life. The Chandra data, presented in captivating colors of red, purple, blue, and white, highlights the energetic phenomena within this stellar nursery, while the optical data is depicted in vibrant green and violet tones. Together, they create a breathtaking representation of young stars, which appear like luminous blue and white jewels, nestled within swirling clouds of gas that mimic the look of “pine needles.”
The image not only showcases the beauty of NGC 2264 but also serves as a reminder of the complexities of star formation and the vastness of our universe. As the cosmos continues to unfold its secrets, this remarkable view of the “Christmas tree cluster” ignites our curiosity about what else lies beyond the stars.
Unlocking the Cosmic Beauty of NGC 2264: Insights and Innovations
Introduction to NGC 2264
NGC 2264, affectionately known as the “Christmas Tree Cluster,” is a stunning stellar formation located approximately 2,500 light-years away from Earth in the constellation Monoceros. This luminous cluster is not just a visual marvel but a significant site for understanding the early stages of star formation.
Features of NGC 2264
1. Youthful Stars: The cluster is home to young stars, estimated to be between one and five million years old. This youthfulness offers astronomers a unique opportunity to study the processes involved in star birth and evolution.
2. Diverse Stellar Population: NGC 2264 houses a wide variety of stars, including massive O-type stars and lower-mass T Tauri stars, each playing a role in the cluster’s dynamic environment.
3. Complex Nebular Structure: Surrounding the stars is a rich environment of gas and dust. The intricate nebulae not only provide material for further star formation but also are sites of intense astrophysical activity.
Observational Techniques
Recent advancements in observational technology have allowed researchers to capture stunning images of NGC 2264.
– X-ray Observations: NASA’s Chandra X-ray Observatory provided crucial X-ray data that highlight energetic processes at play within the cluster. X-ray observations are essential for identifying high-energy phenomena associated with stellar activity.
– Optical Imaging: Combining optical data captured by astrophotographer Michael Clow has enabled a deeper exploration of the region. The use of advanced imaging techniques adds depth and enhances the understanding of the cluster’s structure.
Use Cases of NGC 2264 in Research
– Star Formation Studies: NGC 2264 serves as a key site for studying how stars form in clusters. The interaction between young stars and their surrounding gas and dust is pivotal in understanding stellar nurseries.
– Testing Theories of Stellar Evolution: By observing different types of stars within NGC 2264, researchers can refine their models of stellar evolution and the lifecycle of stars.
Pros and Cons of Studying NGC 2264
Pros:
– Rich Data Source: Offers a wealth of information about the mechanics of star formation and stellar evolution.
– Beautiful Visuals: The aesthetics of NGC 2264 promote public interest and engagement in astrophysics.
Cons:
– Distance and Accessibility: Being located 2,500 light-years away poses challenges in direct observation and immediate study.
– Complex Environment: The chaotic nature of star formation can complicate analyses, requiring sophisticated models to interpret data accurately.
Innovations in Astronomy Inspired by NGC 2264
Recent findings not only enhance our understanding of NGC 2264 but also push the boundaries of astronomical research. The intersection of X-ray astronomy and optical imaging is paving the way for new methodologies in astrophysics that could revolutionize how we observe and interpret cosmic phenomena.
Security and Sustainability in Astrophysics
As the field advances, a focus on the sustainability of observational facilities and data security becomes paramount. Protecting valuable astronomical data and ensuring that research practices are environmentally responsible are ongoing concerns in the astronomical community.
Trends in Stellar Research
The fascination with NGC 2264 is part of a broader trend in astronomy towards understanding star formation in a variety of environments. With the advent of next-generation astronomical instruments, the future of research in clusters like NGC 2264 looks promising, potentially uncovering more secrets about the universe.
Conclusion
The “Christmas Tree Cluster” continues to capture the imagination of astronomers and enthusiasts alike. As new tools and techniques are developed, NGC 2264 will remain a pivotal point of study in uncovering the mysteries of star formation in our universe.
For more information on current astronomical discoveries, visit NASA.