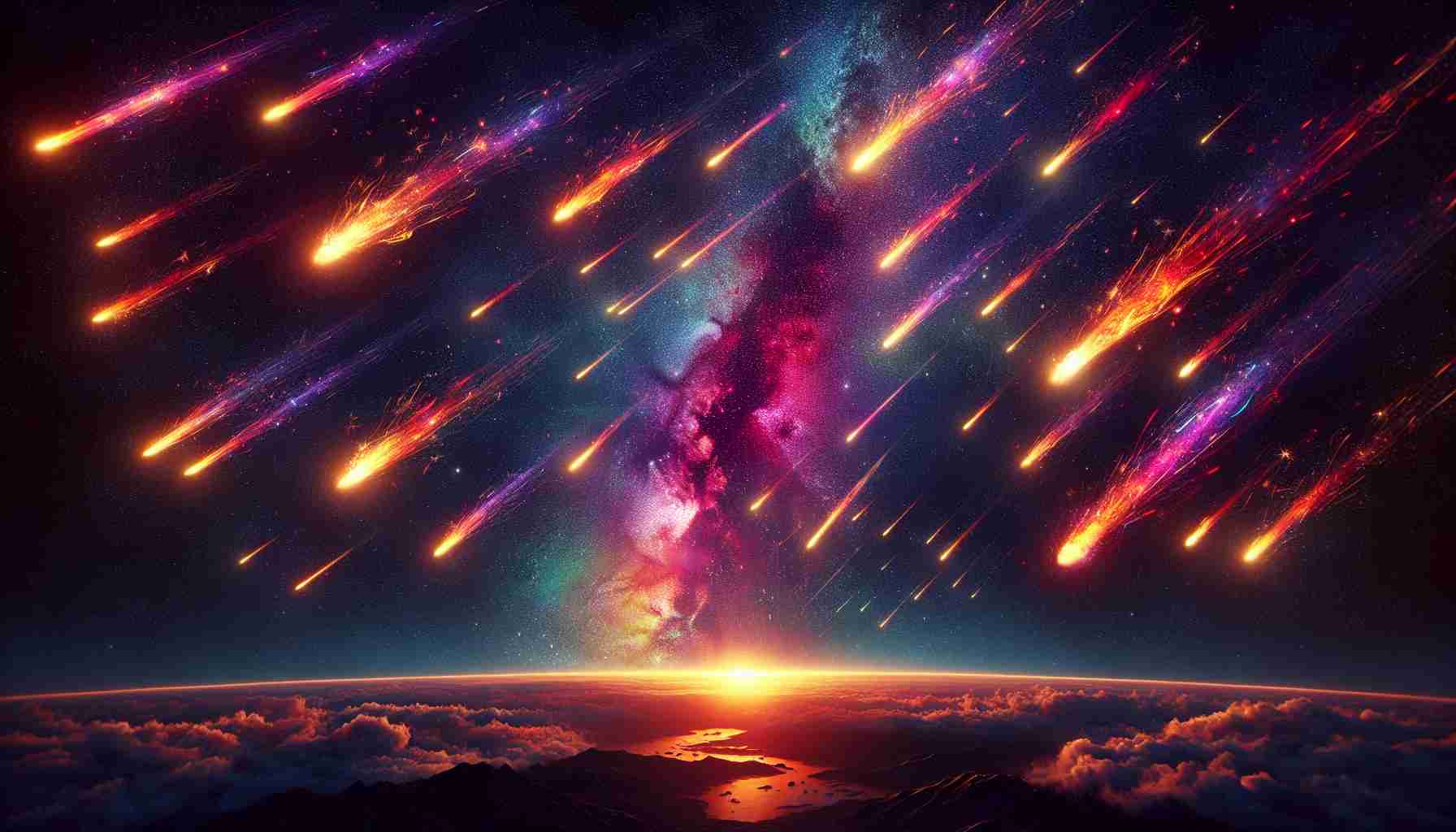
Get Ready for a Celestial Spectacle
A dazzling event is set to grace the night sky as the Quadrantid meteor shower reaches its peak tonight. Although not as widely recognized as other meteor showers, this phenomenon occurs annually from December 26, 2024, to January 16, 2025, providing a unique opportunity for stargazers.
Expect an Amazing Display
When conditions are right, viewers could witness around 25 meteors per hour. Some of these meteors are exceptionally bright fireballs, casting a fleeting glow across the night sky. The prime time for viewing is just before dawn on January 3, 2025, although enthusiasts located in the western regions are likely to enjoy the most meteor sightings.
Understanding the Source
The Quadrantids originate from the asteroid 2003 EH1, which takes 5.5 years to orbit the sun. As Earth passes through the debris trail left by this asteroid, the influx of tiny particles entering our atmosphere generates the spectacular light show. The highest concentrations of meteors occur during the night from January 3 to January 4.
Optimal Viewing Conditions
A crescent moon will set early, making for darker skies—ideal for meteor observation. Stargazers are encouraged to seek areas with minimal light pollution for the best experience. The Quadrantid meteors, while lesser-known, offer a breathtaking treat that won’t be matched until the spring meteor showers. Don’t miss your chance to catch this incredible display!
Catch the Celestial Magic: Your Guide to the Quadrantid Meteor Shower 2025
Introduction to the Quadrantid Meteor Shower
The Quadrantid Meteor Shower is a lesser-known but spectacular astronomical event that occurs annually, peaking between late December and early January. For stargazers, this meteor shower provides a unique spectacle, especially in 2025 when it is expected to produce some of the most dazzling displays in recent years.
Key Features of the Quadrantid Meteor Shower
– Peak Activity: The Quadrantids usually reach their peak activity between January 3 and January 4. The best time to observe is just before dawn, when the skies are darkest.
– Meteor Frequency: Under perfect viewing conditions, enthusiasts may witness up to 25 meteors per hour, including bright fireballs that leave a lasting impression across the night sky.
– Origin: The meteors are remnants from asteroid 2003 EH1, which has a swift orbit around the sun, contributing to the rich collection of debris that produces these meteors when Earth passes through it.
Viewing Conditions and Tips
To maximize your viewing experience, consider the following:
– Timing: Aim for the early hours before dawn, particularly between January 3 and January 4, when meteors are most prevalent.
– Location: Seek out areas away from city lights and with minimal light pollution. National parks or rural locations often provide the best viewing opportunities.
– Weather Checking: Ensure the weather forecast predicts clear skies, as cloud cover can obstruct visibility.
– Equipment: While the meteors can be viewed with the naked eye, binoculars or telescopes may enhance the experience, allowing you to observe constellations and other celestial phenomena.
Pros and Cons of the Quadrantid Meteor Shower
Pros:
– Unique opportunity to witness a high-volume meteor shower.
– Bright fireballs make for an exciting skywatching experience.
– Accessibility; can be seen from most places without special equipment.
Cons:
– The peak is relatively brief, lasting only a few hours.
– Light pollution can significantly reduce visibility, necessitating travel to darker areas.
Innovations in Meteor Watching
In recent years, technology has advanced meteor observation:
– Smartphone Apps: Numerous apps provide real-time tracking and alerts for peak meteor activity, enhancing the stargazing experience.
– Virtual Reality: Some projects simulate meteor showers, allowing users to experience the phenomenon in urban settings where visibility is limited.
Security and Sustainability Aspects
As public interest in celestial events grows, it’s essential to consider the ecological impact of stargazing:
– Preserving Natural Habitats: Outdoor enthusiasts should be mindful of their impact when choosing viewing locations, avoiding disturbances to wildlife and natural ecosystems.
– Digital Preservation: With the advent of virtual stargazing options, individuals can explore the cosmos from home, reducing the need for travel and its associated carbon footprint.
Final Thoughts
The Quadrantid Meteor Shower may not be as famous as others, yet it offers a spectacular show worth the effort. Mark your calendars for the early hours of January 3 and January 4, 2025, and prepare for a memorable celestial experience!
For more information on astronomical events, visit Space.com for current updates and detailed guides.