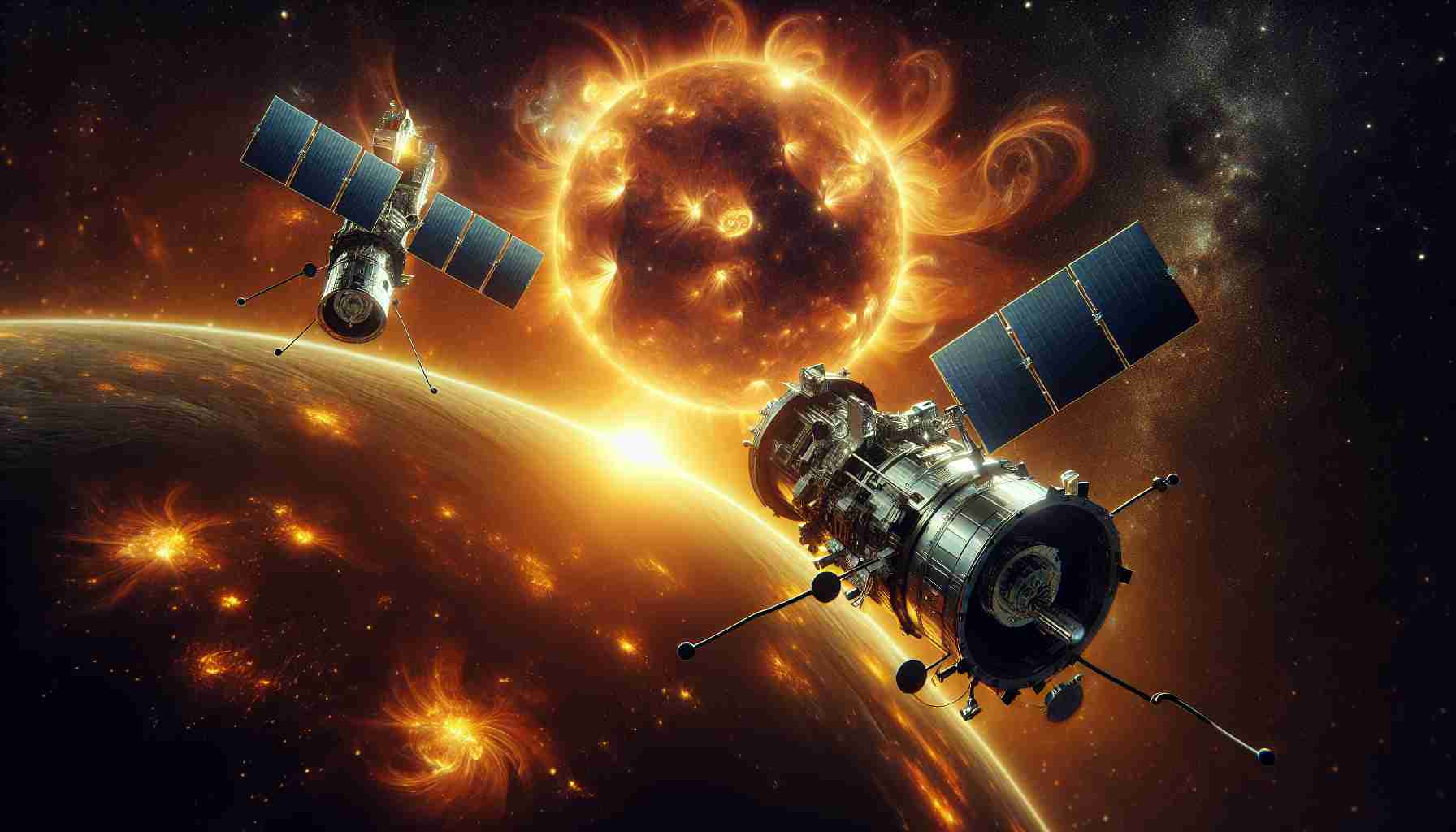
In an exciting breakthrough for solar research, two European satellites launched from India are prepared to transform our understanding of the sun by orchestrating artificial solar eclipses. This innovative mission features the satellites flying in a meticulously planned formation, with one satellite casting a shadow over the other for an impressive six hours—far longer than any natural solar eclipse experienced on Earth. This extraordinary duration offers scientists unparalleled opportunities to investigate the sun’s corona, which is integral to comprehending solar activity and phenomena that could disrupt power systems on our planet.
The mission, termed Proba-3, serves as a demonstration of advanced technology, with the satellites maintaining a precise distance of 492 feet apart. Employing cutting-edge GPS and laser systems ensures their exact alignment. The European Space Agency’s technology director emphasized the significant scientific implications of this project. Over the course of two years, the mission is designed to generate hundreds of artificial eclipses, with initial findings expected to emerge by March next year following rigorous equipment testing.
With a budget of $210 million, Proba-3 promises to shed light on why the corona is hotter than the sun’s surface while simultaneously piloting high-precision formation flying technology—laying the groundwork for future space exploration initiatives. Following the conclusion of this two-year mission, the satellites will re-enter Earth’s atmosphere, culminating their journey in a spectacular display.
Exploring the Sun: The Game-Changing Proba-3 Mission Opens New Frontiers in Solar Research
Introduction
The ongoing Proba-3 mission, launched by the European Space Agency (ESA) from India, marks a significant leap in our quest to understand the sun and its influence on Earth. By executing artificial solar eclipses, this innovative endeavor is poised to revolutionize solar research and enhance our capability to predict solar events that can impact technology and infrastructure on our planet.
Features of the Proba-3 Mission
The Proba-3 mission entails two satellites that fly in tandem, maintaining a staggering distance of 492 feet apart, allowing one to cast a shadow over the other for a lasting six hours. This extended duration allows scientists to study the solar corona’s dynamics under conditions previously unattainable with natural solar eclipses. The use of advanced technologies—GPS and laser systems—ensures their precise coordination, showcasing the mission’s engineering prowess.
Key Specifications
– Distance Between Satellites: 492 feet
– Mission Duration: Two years
– Budget: $210 million
– Expected Initial Findings Release: March 2024
Benefits and Use Cases
Scientific Advancements
The primary focus of the Proba-3 mission is to investigate crucial questions regarding the solar corona, such as:
– Why is the corona hotter than the sun’s surface?
– How do solar activities influence geospace conditions?
This research will be vital in predicting solar wind events and coronal mass ejections (CMEs), which can severely disrupt satellite operations, telecommunications, and power grids on Earth.
Technological Innovation
The mission not only contributes to solar science but also sets a high standard for future space missions through its high-precision formation flying technology, which could pave the way for advanced mult-satellite coordination in various scientific fields, including Earth observation, climate monitoring, and planetary exploration.
Pros and Cons
Pros
– Enhanced Understanding of Solar Phenomena: Extended eclipses allow for in-depth study of the sun’s behavior.
– Advancement of Space Technology: Demonstrates cutting-edge formation flying techniques that may benefit other missions.
– Potential for Real-Time Monitoring: Better predictions of solar events lead to preparedness and mitigation of their impacts on Earth.
Cons
– Cost Factor: The mission’s $210 million budget raises discussions around resource allocation in space research.
– Limited Duration: After two years, the mission’s findings are constrained to the operational timeline, though the insights gained are invaluable.
Market Analysis and Future Trends
As the demand for reliable space weather forecasts grows in tandem with our increasing reliance on technology, the Proba-3 mission appears to be a timely investment. Analysts predict that ongoing research will spur advancements not only in solar astrophysics but also in related areas such as telecommunications and materials science, enhancing the resilience of global infrastructure against solar phenomena.
Security and Sustainability Aspects
The Proba-3 mission emphasizes sustainable practices by relying on innovative satellite technology to minimize space debris. This proactive approach to space exploration ensures that future generations can also benefit from the advancements in solar research without compromising the integrity of near-Earth space.
Conclusion
The Proba-3 mission is not merely an experiment in formation flying but a significant step forward in our understanding of solar dynamics. With the first results expected soon, the scientific community is eager to see the outcomes that will emerge from these artificial eclipses. As we look to the future, the knowledge gained from this mission will undoubtedly have profound implications for solar research and its applications on Earth.
For more detailed insights on space exploration initiatives, visit the European Space Agency.